Base-N App
The Base-N application batch returns the results of a calculation in hexadecimal, decimal, octal, and binary form. The calculation can be input using hexadecimal, decimal, octal, or binary numbers.
In this chapter, subscripts are appended to values to indicate the radix of the value. For example, means hexadecimal 1.
Basic Calculation Operations
To start a calculation
-
h > Base-N
-
Use F to select a number system (base).
-
Input the calculation and then press E.
This causes the input cursor to appear in the upper left corner of the app window.
Each press of F cycles the number system setting in the sequence: [Decimal] → [Hexadecimal] → [Binary] → [Octal]. The currently selected number system is shown in line two of the app window.
The calculation result is displayed in Hex (hexadecimal), Dec (decimal), Oct (octal), and Bin (binary) form.
Inputting Values
The letters A through F for hexadecimal values can be entered using key input or menu input.
XA, eB, jC, gD, iE, NF or C > [Hex Value] > [A], [B], [C], [D], [E], [F]
You can specify the number system for any value in a calculation by including d, h, b, or o before the value.
C > [Base Prefix] > [d], [h], [b], [o] (d: Decimal, h: Hexadecimal, b: Binary, o: Octal)
Example: d10 is treated as . b111 is treated as .
Input of decimal fractions and exponents is not supported. If a calculation result produces a decimal fraction or exponent, the decimal fraction or exponent will be cut off.
Example Calculation
|
F > [Binary] |
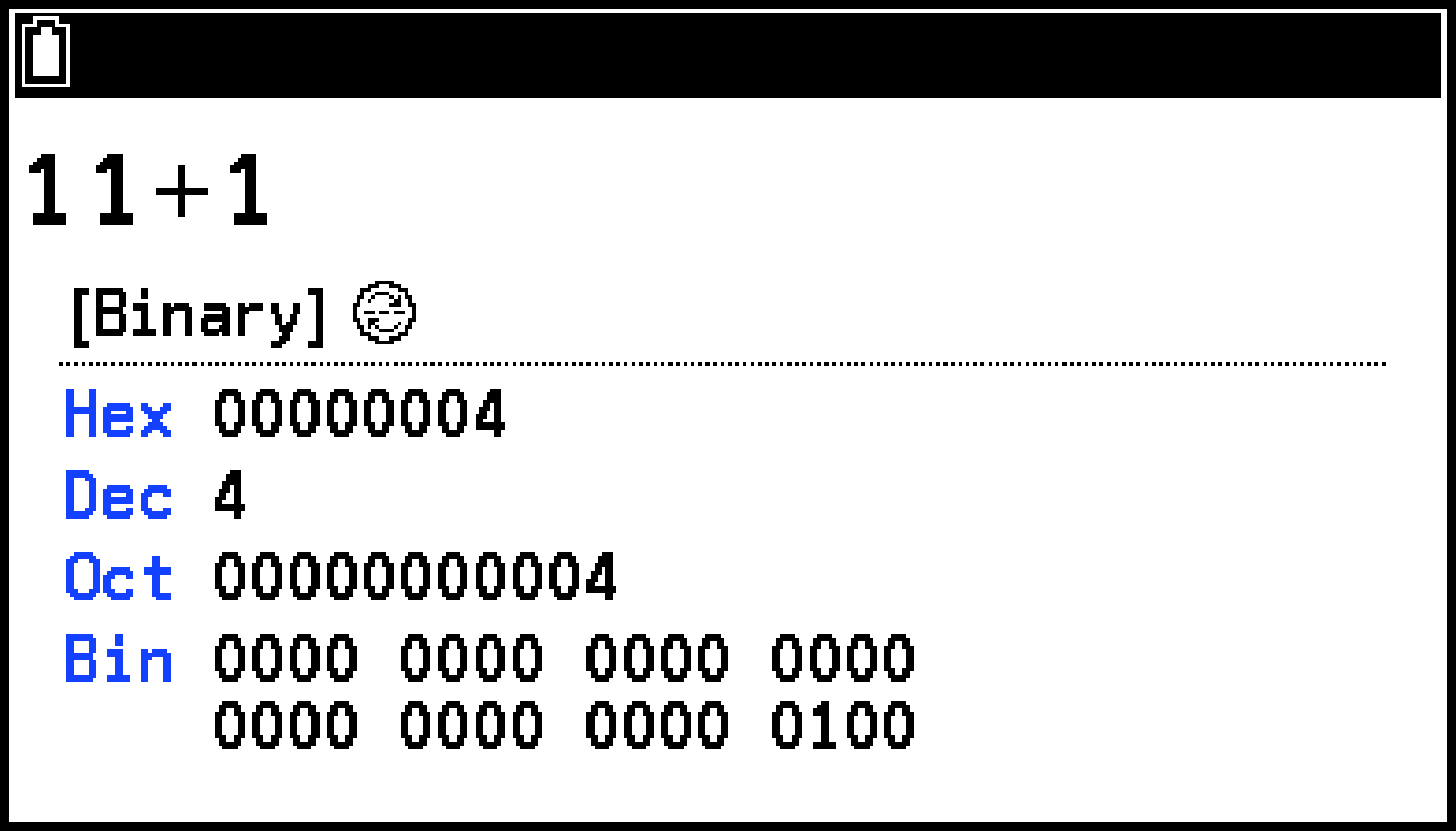 |
|
|
F > [Hexadecimal] |
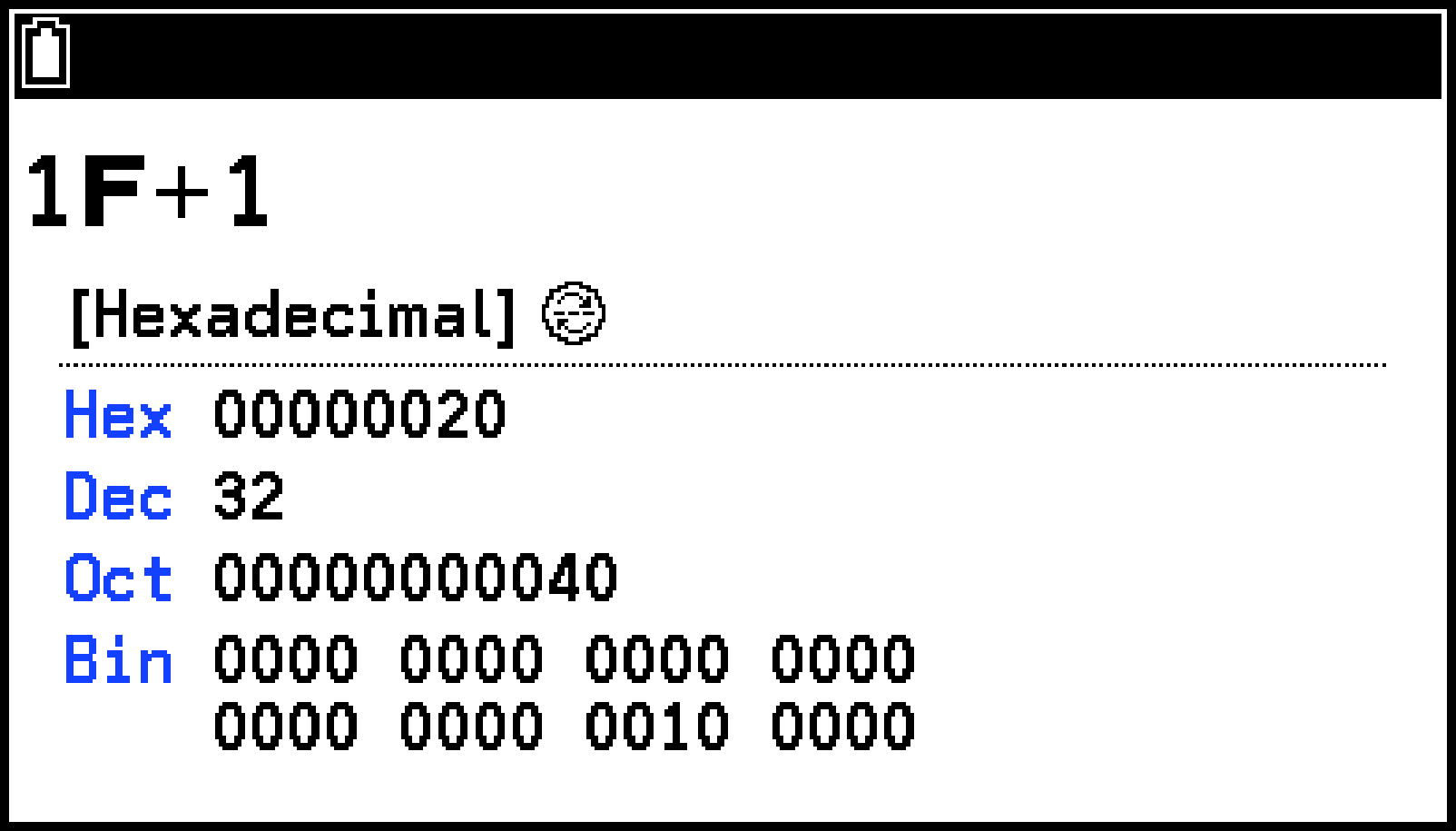 |
|
|
F > [Decimal] |
 |
Latest Calculation Result (Ans)
The result of the latest calculation is stored in a variable named Ans, which is independent of the Calculate app’s Ans. To input Ans into a new calculation, press PF(Ans).
Pressing F clears the calculation and all results, but Ans retains the latest calculation result.
The Base-N app’s Ans is reset to 0 each time you exit the Base-N app.
Logical Operations and Negative Number Calculations
The following functions and commands can perform logical (bitwise operations) and negative number calculations.
C > [Logic Operation] > [Neg()], [Not()], [and], [or], [xor], [xnor]
Syntax
|
Neg() |
Obtains the negative value*1 of . |
|
Not() |
Negates*2 . |
|
and |
Obtains the logical conjunction*3 of and . |
|
or |
Obtains the logical disjunction*3 of and . |
|
xor |
Obtains the exclusive OR*3 of and . |
|
xnor |
Negates*3 the exclusive OR of and . |
Two’s complement. Negative binary, octal, and hexadecimal values are produced by taking the two’s complement of a 32-bit binary number and then returning the result to the original number base. With the decimal number base, negative values are displayed with a minus sign.
One’s complement (bitwise complement)
Bitwise AND, bitwise OR, bitwise XOR, bitwise XNOR
Example Calculation
Logical Operators
|
To obtain the result of and |
F > [Hexadecimal] |
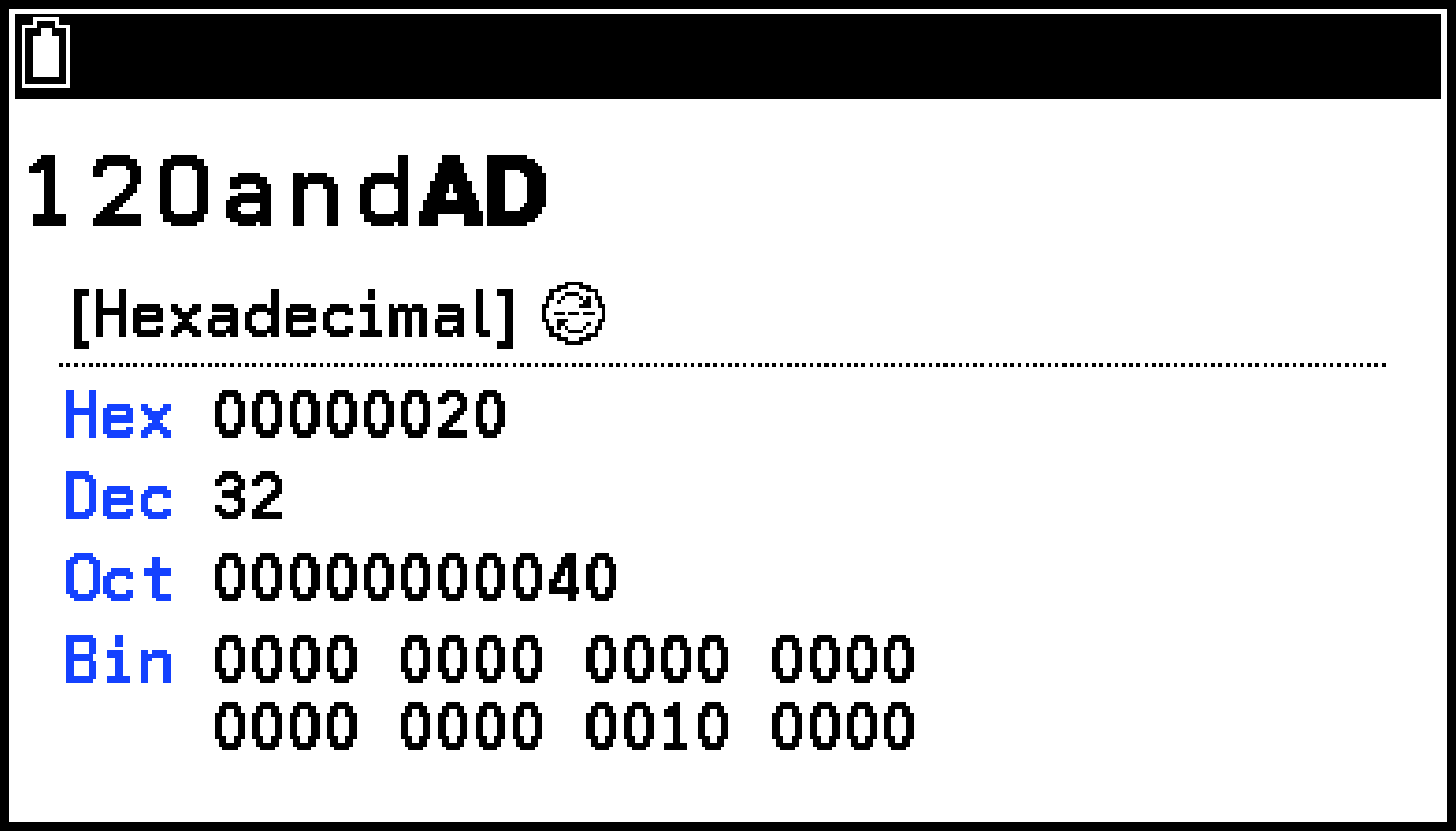 |
Negative Value Calculations
|
To obtain the negative value of |
F > [Binary] |
 |
Input/Output Ranges
Input and output ranges for each number system are shown below (32 bits).
|
Base |
Input/Output Range |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Binary |
Positive: |
00000000000000000000000000000000 ≤ ≤ 01111111111111111111111111111111 |
|
Negative: |
10000000000000000000000000000000 ≤ ≤ 11111111111111111111111111111111 |
|
|
Octal |
Positive: |
00000000000 ≤ ≤ 17777777777 |
|
Negative: |
20000000000 ≤ ≤ 37777777777 |
|
|
Decimal |
-2147483648 ≤ ≤ 2147483647 |
|
|
Hexadecimal |
Positive: |
00000000 ≤ ≤ 7FFFFFFF |
|
Negative: |
80000000 ≤ ≤ FFFFFFFF |
|