Base-n Calculations
When you want to perform calculations using decimal, hexadecimal, binary, and/or octal values, launch the Base-N app. Press  , select the Base-N app icon, and then press
, select the Base-N app icon, and then press  . The initial default number mode setting when you launch the Base-N app is decimal.
. The initial default number mode setting when you launch the Base-N app is decimal.
After launching the Base-N app, use  to switch number modes.
to switch number modes.
Each press of  cycles through the number modes as shown below.
cycles through the number modes as shown below.

(1) [Decimal]
(2) [Hexadecimal]
(3) [Binary]
(4) [Octal]
Note
The subscripts appended to the values shown in the examples indicate the base (number mode) of each value.
Example: 12 ... Binary 1; 116 ... Hexadecimal 1
Example 1: To calculate 112 + 12
1. Use  to change the number mode to [Binary].
to change the number mode to [Binary].
2. Perform the calculation 112 + 12.
- 11
 1
1

Example 2: To calculate 1F16 + 116 in hexadecimal
1. Use  to change the number mode to [Hexadecimal].
to change the number mode to [Hexadecimal].
2. Perform the calculation 1F16 + 116.
- 1

 (F)
(F) 1
1

Note
Use the following keys to input the letters A through F for hexadecimal values: 
 (A),
(A), 
 (B),
(B), 
 (C),
(C), 
 (D),
(D), 
 (E),
(E), 
 (F). You can also input hexadecimal values using the CATALOG menu items shown below.
(F). You can also input hexadecimal values using the CATALOG menu items shown below.
 – [Hex Value] > [A], [B], [C], [D], [E], or [F]
– [Hex Value] > [A], [B], [C], [D], [E], or [F]
Note that if you input any character from A through F using the operation below, the character will be treated as a variable name, and not as a hexadecimal value.
(1) Press  to display the variable list screen.
to display the variable list screen.
(2) Select [A=], [B=], [C=], [D=], [E=], or [F=], and then press  .
.
(3) On the menu that appears, select [Recall].
In the Base-N app, input of fractional (decimal) values and exponents is not supported. If a calculation result has a fractional part, it is cut off.
Details about input and output ranges (32 bits) are shown below.
| Base | Range |
|---|---|
| Binary | Positive: 00000000000000000000000000000000 ≤ x ≤ 01111111111111111111111111111111 Negative: 10000000000000000000000000000000 ≤ x ≤ 11111111111111111111111111111111 |
| Octal | Positive: 00000000000 ≤ x ≤ 17777777777 Negative: 20000000000 ≤ x ≤ 37777777777 |
| Decimal | -2147483648 ≤ x ≤ 2147483647 |
| Hexadecimal | Positive: 00000000 ≤ x ≤ 7FFFFFFF Negative: 80000000 ≤ x ≤ FFFFFFFF |
A Math ERROR occurs when a calculation result is outside the applicable range for the number system being used.
Specifying the Number Mode of a Particular Input Value
You can input a special command immediately before a value to specify the number mode of that value. The special commands are: d (decimal), h (hexadecimal), b (binary), and o (octal).
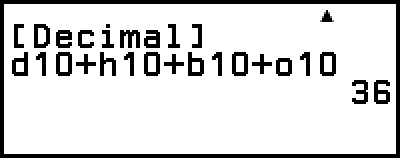
Example 3: To calculate 1010 + 1016 + 102 + 108 and display the result as a decimal value
1. Use  to change the number mode to [Decimal].
to change the number mode to [Decimal].
2. Perform the calculation 1010 + 1016 + 102 + 108.
 – [Base Prefix] > [Decimal(d)] 10
– [Base Prefix] > [Decimal(d)] 10
 – [Base Prefix] > [Hexadecimal(h)] 10
– [Base Prefix] > [Hexadecimal(h)] 10
 – [Base Prefix] > [Binary(b)] 10
– [Base Prefix] > [Binary(b)] 10
 – [Base Prefix] > [Octal(o)] 10
– [Base Prefix] > [Octal(o)] 10
Converting a Calculation Result to Another Type of Value
You can use  to convert the currently displayed calculation result to another type of value.
to convert the currently displayed calculation result to another type of value.
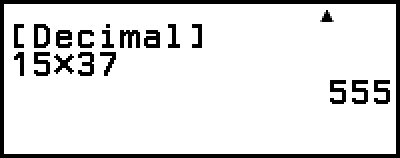
Example 4: To calculate 1510 × 3710 in the decimal mode, and then convert the result to hexadecimal
1. Use  to change the number mode to [Decimal].
to change the number mode to [Decimal].
2. Perform the calculation 1510 × 3710.
- 15
 37
37
3. Use  to change the number mode to [Hexadecimal].
to change the number mode to [Hexadecimal].
Logical and Negation Operations
Logical and negation operations are performed by pressing  and selecting [Logic Operation], and then selecting the desired command (Neg, Not, and, or, xor, xnor) from the menu that appears. All of the examples below are performed in the binary mode.
and selecting [Logic Operation], and then selecting the desired command (Neg, Not, and, or, xor, xnor) from the menu that appears. All of the examples below are performed in the binary mode.
Example 5: To determine the logical AND of 10102 and 11002 (10102 and 11002)
- 1010
 – [Logic Operation] > [and]
– [Logic Operation] > [and]
1100
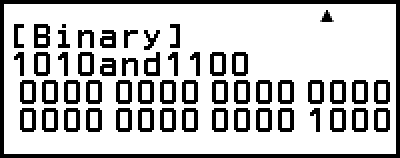
Example 6: To determine the bitwise complement of 10102 (Not(10102))
 – [Logic Operation] > [Not]
– [Logic Operation] > [Not]
1010


Note
In the case of a negative binary, octal or hexadecimal value, the calculator converts the value to binary, takes the two’s complement, and then converts back to the original number base. For decimal values, the calculator merely adds a minus sign.

