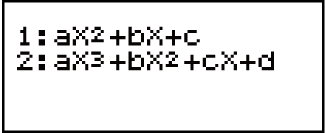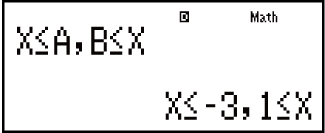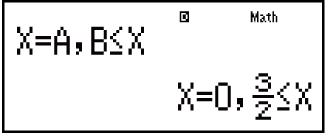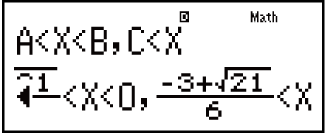fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
You can use the following procedure to solve a quadratic inequality or cubic inequality.
1. Press 

 (INEQ) to enter the INEQ Mode.
(INEQ) to enter the INEQ Mode.
2. On the menu that appears, select an inequality type.
| To select this inequality type: | Press this key: |
|---|---|
| Quadratic inequality |  (aX2 + bX + c) (aX2 + bX + c) |
| Cubic inequality |  (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d) (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d) |
3. On the menu that appears, use keys  through
through  to select the inequality symbol type and orientation.
to select the inequality symbol type and orientation.
4. Use the Coefficient Editor that appears to input coefficient values.
To solve x2 + 2x - 3 < 0, for example, input the coefficients a = 1, b = 2, c = -3 by pressing 1 2
2
 3
3 .
.
To change a coefficient value you already have input, move the cursor to the appropriate cell, input the new value, and then press  .
.
Pressing  will clear all of the coefficients to zero.
will clear all of the coefficients to zero.
Note: The following operations are not supported by the Coefficient Editor:  ,
, 
 (M-),
(M-), 
 (STO). Pol, Rec, ÷R, and multi-statements also cannot be input with the Coefficient Editor.
(STO). Pol, Rec, ÷R, and multi-statements also cannot be input with the Coefficient Editor.
5. After all the values are the way you want, press  .
.
This will display the solutions.
To return to the Coefficient Editor while the solutions are displayed, press  .
.
Note
Values cannot be converted to engineering notation on the solution screen.
Changing the Inequality Type
Press 

 (INEQ) and then select an inequality type from the menu that appears. Changing the inequality type causes the values of all Coefficient Editor coefficients to change to zero.
(INEQ) and then select an inequality type from the menu that appears. Changing the inequality type causes the values of all Coefficient Editor coefficients to change to zero.
INEQ Mode Calculation Examples
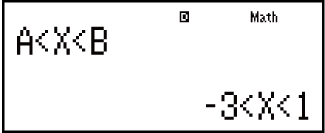
Example 1: x2 + 2x - 3 < 0 (MthIO-MathO)


 (INEQ)
(INEQ) (aX2 + bX + c)
(aX2 + bX + c)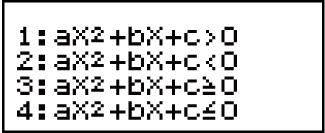
 (aX2 + bX + c < 0)
(aX2 + bX + c < 0)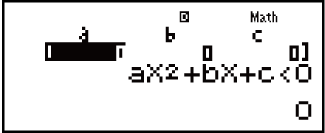
- 1
 2
2
 3
3
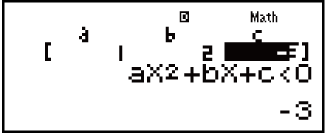
Example 2: x2 + 2x - 3 ≧ 0 (MthIO-MathO)


 (INEQ)
(INEQ) (aX2 + bX + c)
(aX2 + bX + c)
 (aX2 + bX + c ≧ 0)
(aX2 + bX + c ≧ 0)
1 2
2
 3
3
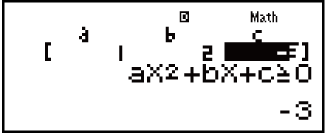
- Note: Solutions are displayed as shown here when Linear Display is selected.
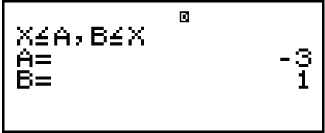
Example 3: 2x3 - 3x2 ≧ 0 (MthIO-MathO)


 (INEQ)
(INEQ) (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d)
(aX3 + bX2 + cX + d)
 (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d ≧ 0)
(aX3 + bX2 + cX + d ≧ 0)
2
 3
3
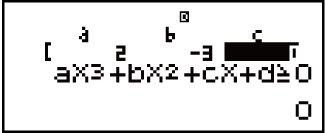
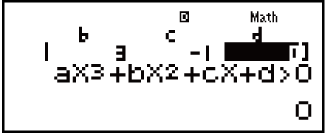
Example 4: 3x3 + 3x2 - x > 0 (MthIO-MathO)


 (INEQ)
(INEQ) (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d)
(aX3 + bX2 + cX + d)
 (aX3 + bX2 + cX + d > 0)
(aX3 + bX2 + cX + d > 0)
3 3
3
 1
1
- Note: Solutions are displayed as shown here when Linear Display is selected.
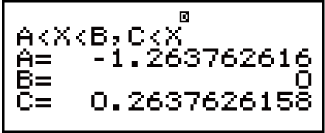
Special Solution Display
"All Real Numbers" appears on the solution screen when the solution of an inequality is all numbers.
Example: x2 ≧ 0 (MthIO-MathO)


 (INEQ)
(INEQ) (aX2 + bX + c)
(aX2 + bX + c)
 (aX2 + bX + c ≧ 0)
(aX2 + bX + c ≧ 0)
1 0
0 0
0


"No-Solution" appears on the solution screen when no solution exists for an inequality (such as X2 < 0).