fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Remainder Calculations
You can use the ÷R function to obtain the quotient and remainder in a division calculation.
Example: To calculate the quotient and remainder of 5 ÷ 2 (quotient = 2, remainder = 1)
(MthIO-MathO)
5
 (÷R) 2
(÷R) 2
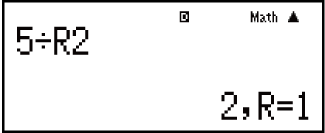
(LineIO)
5
 (÷R) 2
(÷R) 2

Note
Only the quotient value of a ÷R calculation is stored in Ans memory.
Assigning the result of a remainder division calculation to a variable will assign the quotient value only. Performing the operation 5
 (÷R) 2
(÷R) 2
 (STO)
(STO) (X) (which assigns the result of 5÷R2 to X) will assign a value of 2 to X.
(X) (which assigns the result of 5÷R2 to X) will assign a value of 2 to X.
If a ÷R calculation is part of a multi-step calculation, only the quotient is passed on to the next operation.
Example: 10 17
17
 (÷R) 6
(÷R) 6 → 10
→ 10 2
2 → 12
→ 12
Operation of the  and
and  keys is disabled while a remainder division result is on the display.
keys is disabled while a remainder division result is on the display.
Cases when Remainder Division becomes Non-remainder Division
If either of the conditions below exists when you perform a remainder division operation, the calculation will be treated as normal (non-remainder) division.
When either the dividend or the divisor is a very large value
Example: 20000000000
 (÷R) 17
(÷R) 17
→ Calculated as: 20000000000 ÷ 17
When the quotient is not a positive integer, or if the remainder is not a positive integer or positive fractional value
Example:  5
5
 (÷R) 2
(÷R) 2 → Calculated as: -5 ÷ 2
→ Calculated as: -5 ÷ 2