fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
TABLE generates a numerical table based on one or two functions. You can use the function f(x) or the two functions f(x) and g(x). See "Configuring the Calculator Setup" for more information.
Perform the following steps to generate a numerical table.
1. Press 
 (TABLE) to enter the TABLE Mode.
(TABLE) to enter the TABLE Mode.
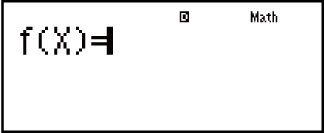
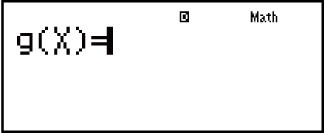
2. Use the X variable to input two functions, one in the format f(x) and the other in the format g(x).
Be sure to input the X variable (
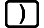 (X)) when generating a numerical table. Any variable other than X is handled as a constant.
(X)) when generating a numerical table. Any variable other than X is handled as a constant.
If you are using a single function, input a function in the format f(x) only.
The following cannot be used in the function: Pol, Rec, ∫, d/dx, Σ, Π.
3. In response to the prompts that appear, input the values you want to use, pressing  after each one.
after each one.
| For this prompt: | Input this: |
|---|---|
| Start? | Input the lower limit of X (Default = 1). |
| End? | Input the upper limit of X (Default = 5). Note: Make sure that the End value is always greater than the Start value. |
| Step? | Input the increment step (Default = 1). Note: The Step specifies by how much the Start value should be sequentially incremented as the numerical table is generated. If you specify Start = 1 and Step = 1, X sequentially will be assigned the values 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on to generate the numerical table until the End value is reached. |
Inputting the Step value and pressing  generates and displays the numerical table in accordance with the parameters you specified.
generates and displays the numerical table in accordance with the parameters you specified.
Pressing  while the numerical table screen is displayed will return to the function input screen in step 2.
while the numerical table screen is displayed will return to the function input screen in step 2.
Example: To generate a numerical table for the functions f(x) = x2 + 12 and g(x) = x2 - 12 for the range -1 ≦ x ≦ 1, incremented in steps of 0.5 (MthIO-MathO)

 (TABLE)
(TABLE)
 (SETUP)
(SETUP)
 (TABLE)
(TABLE) (f(x),g(x))
(f(x),g(x))

 (X)
(X)
 1
1 2
2
- ・Pressing
 without inputting anything for g(x) will generate a numerical table based on f(x) only.
without inputting anything for g(x) will generate a numerical table based on f(x) only.

 (X)
(X)
 1
1 2
2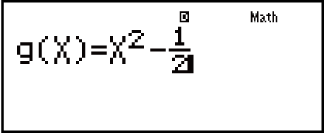

 1
1 1
1 0
0 5
5

Note
You can use the numerical table screen for viewing values only. Table contents cannot be edited.
The numerical table generation operation causes the contents of variable X to be changed.
The maximum number of rows in the generated numerical table depends on the setup menu table setting. Up to 30 rows are supported for the "f(x)" setting, while 20 rows are supported for the "f(x),g(x)" setting.
Important!
The function you input for numerical table generation is deleted whenever you display the setup menu in the TABLE Mode and switch between Natural Display and Linear Display.