fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Scientific Constants
Your calculator comes with 40 built-in scientific constants that can be used in any mode besides BASE-N.
Each scientific constant is displayed as a unique symbol (such as π), which can be used inside of calculations.
To input a scientific constant into a calculation, press 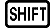
 (CONST) and then input the two-digit number that corresponds to the constant you want.
(CONST) and then input the two-digit number that corresponds to the constant you want.
Example 1: To input the scientific constant C0 (speed of light in a vacuum), and display its value

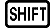
 (CONST)
(CONST)

 (C0)
(C0)

Example 2: To calculate C0 = 1 √ε0μ0 (MthIO-MathO)

 1
1

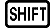
 (CONST)
(CONST)
 (ε0)
(ε0)
 (CONST)
(CONST)
 (μ0)
(μ0)

The following shows the two-digit numbers for each of the scientific constants.
| 01: (mp) proton mass | 02: (mn) neutron mass |
|---|---|
| 03: (me) electron mass | 04: (mμ) muon mass |
| 05: (a0) Bohr radius | 06: (h) Planck constant |
| 07: (μN) nuclear magneton | 08: (μB) Bohr magneton |
09: (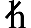 ) Planck constant, rationalized ) Planck constant, rationalized |
10: (α) fine-structure constant |
| 11: (re) classical electron radius | 12: (λC) Compton wavelength |
| 13: (γp) proton gyromagnetic ratio | 14: (λCp) proton Compton wavelength |
| 15: (λCn) neutron Compton wavelength | 16: (R∞) Rydberg constant |
| 17: (u) atomic mass unit | 18: (μp) proton magnetic moment |
| 19: (μe) electron magnetic moment | 20: (μn) neutron magnetic moment |
| 21: (μμ) muon magnetic moment | 22: (F) Faraday constant |
| 23: (e) elementary charge | 24: (NA) Avogadro constant |
| 25: (k) Boltzmann constant | 26: (Vm) molar volume of ideal gas (237.15K, 100kPa) |
| 27: (R) molar gas constant | 28: (C0) speed of light in vacuum |
| 29: (C1) first radiation constant | 30: (C2) second radiation constant |
| 31: (σ) Stefan-Boltzmann constant | 32: (ε0) electric constant |
| 33: (μ0) magnetic constant | 34: (Φ0) magnetic flux quantum |
| 35: (g) standard acceleration of gravity | 36: (G0) conductance quantum |
| 37: (Z0) characteristic impedance of vacuum | 38: (t) Celsius temperature |
| 39: (G) Newtonian constant of gravitation | 40: (atm) standard atmosphere |
The values are based on CODATA (2014) recommended values.