fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Errors
The calculator will display an error message whenever an error occurs for any reason during a calculation.
There are two ways to exit an error message display: Pressing  or
or  to display the location of the error, or pressing
to display the location of the error, or pressing  to clear the message and calculation.
to clear the message and calculation.
Displaying the Location of an Error
While an error message is displayed, press  or
or  to return to the calculation screen. The cursor will be positioned at the location where the error occurred, ready for input. Make the necessary corrections to the calculation and execute it again.
to return to the calculation screen. The cursor will be positioned at the location where the error occurred, ready for input. Make the necessary corrections to the calculation and execute it again.
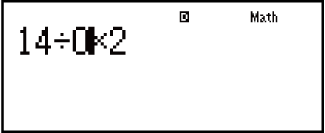
Example: When you input 14 ÷ 0 × 2 by mistake instead of 14 ÷ 10 × 2 (MthIO-MathO)
- 14
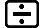 0
0 2
2

 (or
(or  )
)
 1
1
Clearing the Error Message
While an error message is displayed, press  to return to the calculation screen. Note that this also clears the calculation that contained the error.
to return to the calculation screen. Note that this also clears the calculation that contained the error.
Error Messages
Math ERROR
Cause:
The intermediate or final result of the calculation you are performing exceeds the allowable calculation range.
Your input exceeds the allowable input range (particularly when using functions).
The calculation you are performing contains an illegal mathematical operation (such as division by zero).
Action:
Check the input values, reduce the number of digits, and try again.
When using independent memory or a variable as the argument of a function, make sure that the memory or variable value is within the allowable range for the function.
Stack ERROR
Cause:
The calculation you are performing has caused the capacity of the numeric stack or the command stack to be exceeded.
The calculation you are performing has caused the capacity of the matrix or vector stack to be exceeded.
Action:
Simplify the calculation expression so it does not exceed the capacity of the stack.
Try splitting the calculation into two or more parts.
Syntax ERROR
Cause:
There is a problem with the format of the calculation you are performing.
Action:
Make necessary corrections.
Argument ERROR
Cause:
There is a problem with the argument of the calculation you are performing.
Action:
Make necessary corrections.
Dimension ERROR (MATRIX and VECTOR Modes only)
Cause:
The matrix or vector you are trying to use in a calculation was input without specifying its dimension.
You are trying to perform a calculation with matrices or vectors whose dimensions do not allow that type of calculation.
Action:
Specify the dimension of the matrix or vector and then perform the calculation again.
Check the dimensions specified for the matrices or vectors to see if they are compatible with the calculation.
Variable ERROR (SOLVE feature only)
Cause:
You did not specify a solution variable, and there is no X variable in the equation you input.
The solution variable that you specified is not included in the equation you input.
Action:
The equation you input must include an X variable when you do not specify the solution variable.
Specify a variable that is included in the equation you input as the solution variable.
Can't Solve Error (SOLVE feature only)
Cause:
The calculator could not obtain a solution.
Action:
Check for errors in the equation that you input.
Input a value for the solution variable that is close to the expected solution and try again.
Insufficient MEM Error
Cause:
An attempt to generate a numerical table in the TABLE Mode whose conditions cause it to exceed the maximum number of allowable rows. The maximum number of rows is 30 when "f(x)" is selected for the setup menu table setting and 20 when "f(x),g(x)" is selected.
Action:
Narrow the table calculation range by changing the Start, End, and Step values, and try again.
Time Out Error
Cause:
The current differential or integration calculation ends without the ending condition being fulfilled.
Action:
Try increasing the tol value. Note that this also decreases solution precision.