fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Calculation Priority Sequence
The priority sequence of input calculations is evaluated in accordance with the rules below.
When the priority of two expressions is the same, the calculation is performed from left to right.
| 1 | Parenthetical expressions |
|---|---|
| 2 | Functions that require an argument to the right and a closing parenthesis ")" following the argument |
| 3 | Functions that come after the input value (x2, x3, x-1, x!, °’ ”, °, r, g, %,  t), powers ( t), powers (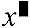 ), roots ( ), roots ( ) ) |
| 4 | Fractions |
| 5 | Negative sign ((-)), base-n symbols (d, h, b, o) |
| 6 | Metric conversion commands (cm in, etc.), STAT Mode estimated values (xˆ, yˆ, xˆ1, xˆ2) in, etc.), STAT Mode estimated values (xˆ, yˆ, xˆ1, xˆ2) |
| 7 | Multiplication where the multiplication sign is omitted |
| 8 | Permutation (nPr), combination (nCr), complex number polar coordinate symbol (∠) |
| 9 | Dot product (•) |
| 10 | Multiplication (×), division (÷), remainder calculations (÷R) |
| 11 | Addition (+), subtraction (-) |
| 12 | and (logical operator) |
| 13 | or, xor, xnor (logical operators) |
Note
When squaring a negative value (such as -2), the value being squared must be enclosed in parentheses (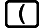
 2
2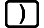

 ). Since x2 has a higher priority than the negative sign, inputting
). Since x2 has a higher priority than the negative sign, inputting  2
2
 would result in the squaring of 2 and then appending a negative sign to the result.
would result in the squaring of 2 and then appending a negative sign to the result.
Always keep the priority sequence in mind, and enclose negative values in parentheses when required.