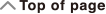fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
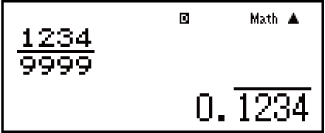
Recurring Decimal Calculations
Your calculator uses a recurring decimal when you input a value. Calculation results also can be displayed using recurring decimal form whenever applicable.
Inputting a Recurring Decimal
When inputting a recurrent decimal, press 
 (
( ) before inputting its period (repetend) and then input the period up to the ending value. To input
the recurring decimal 0.909090.... (0.90), perform the following operation: "0
) before inputting its period (repetend) and then input the period up to the ending value. To input
the recurring decimal 0.909090.... (0.90), perform the following operation: "0

 (
( ) 90".
) 90".
Important!
If the value starts with an integer part (like: 12.3123123...), do not include the integer part when inputting the period (12.312).
Recurring decimal input is possible only when Natural Display is selected.
Example 1: To input 0.33333… (0.3)
- 0



 (
( )
)
- 3

Example 2: To input 1.428571428571... (1.428571) (MthIO-MathO)
- 1


 (
( )
) 
- 428571

Example 3: To calculate 1.021 + 2.312
- 1


 (
( ) 021
) 021

2

 (
( ) 312
) 312
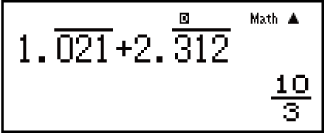
-
Calculation result displayed as recurring decimal value:

Note
You can specify up to 14 decimal places for the recurring decimal period. If you input more than 14 decimal places, the value will be treated as a terminating decimal and not a recurring decimal.
Recurring decimal value input can be performed regardless of the Rdec setting on the setup menu.
Displaying a Calculation Result as a Recurring Decimal Value
Calculation results that can be displayed as recurring decimal values will be displayed as such when ON is selected for the Rdec setting on the setup menu.
Pressing the  key will cycle between the available calculation result formats.
key will cycle between the available calculation result formats.
Example 1: 17 = 0.142857 = 0.1428571429 (Norm 1) (MthIO-MathO)
- 1
 7
7

-
Display as recurring decimal:

-
Decimal value according to Norm 1 setting:


-
Return to initial display format (fraction):


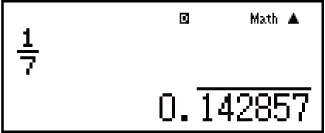
Example 2: 1 ÷ 7 = 17 = 0.142857 = 0.1428571429 (Norm 1) (MthIO-MathO)
- 1
 7
7


-
Display as fraction:


-
Display as recurring decimal:

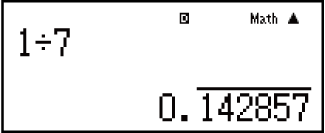
-
Return to initial display format (Norm 1):


Example 3: 17 = 0.142857 = 0.1428571429 (Norm 1) (LineIO)
- 1
 7
7

-
Display as recurring decimal:

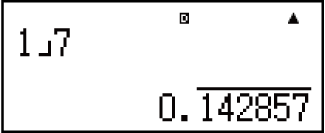
-
Decimal value according to Norm 1 setting:


-
Return to initial display format (fraction):


Example 4: 1 ÷ 7 = 0.1428571429 (Norm 1) = 17 = 0.142857 (LineIO)
- 1
 7
7

-
Display as fraction:


-
Display as recurring decimal:

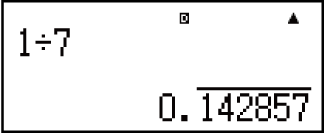
-
Return to initial display format (Norm 1):


Conditions for Displaying a Calculation Result as a Recurring Decimal
If a calculation result satisfies the following conditions, pressing  will
display it as a recurring decimal value.
will
display it as a recurring decimal value.
The total number of digits used in the mixed fraction (including integer, numerator, denominator, and separator symbol) must be no more than 10.
The data size of the value when displayed as a recurring decimal must be no larger than 99 bytes, calculated as: [number of digits (1 byte each)] + [1 byte for the decimal point] + [3 bytes for recurring decimal management code]. For example, the data size of 0.123 would be 4 bytes for digits, 1 byte for the decimal point, and 3 bytes for recurring decimal management code, for a total of 8 bytes.
Note
For information about switching the display format of a calculation result when OFF is selected for the Rdec setting on the setup menu, see "Toggling Calculation Results".
Recurring Decimal Examples
Example 1: 0.3 + 0.45 = 0.78 (MthIO-MathO)
- 0


 (
( ) 3
) 3

0

 (
( ) 45
) 45


Example 2: 1.6 + 2.8 = 4.5 (MthIO-MathO)
- 1


 (
( ) 6
) 6

2

 (
( ) 8
) 8


Example 3: To confirm the following: 0.123 = 123999, 0.1234 = 12349999, 0.12345 = 1234599999 (MthIO-MathO)
- 123
 999
999

- 1234
 9999
9999

- 12345
 99999
99999