fx-115ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS C
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Remainder Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Π Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- ▶Integer Part of a Value (Int) and Largest Integer that does not Exceed a Value (Intg)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from Two Functions (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
- ▶Inequality Calculations (INEQ)
- ▶Using VERIFY (VERIF)
- ▶Distribution Calculations (DIST)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Distribution Calculations (DIST)
You can use the procedures below to perform seven different types of distribution calculations.
1. Press 

 (DIST) to enter the DIST Mode.
(DIST) to enter the DIST Mode.
2. On the menu that appears, select a distribution calculation type.
| To select this type of calculation: | Press this key: |
|---|---|
| Normal probability density |  (Normal PD) (Normal PD) |
| Normal cumulative distribution |  (Normal CD) (Normal CD) |
| Inverse normal cumulative distribution |  (Inverse Normal) (Inverse Normal) |
| Binomial probability |  (Binomial PD) (Binomial PD) |
| Binomial cumulative distribution |   (Binomial CD) (Binomial CD) |
| Poisson probability |   (Poisson PD) (Poisson PD) |
| Poisson cumulative distribution |   (Poisson CD) (Poisson CD) |
3. Input values for the variables.
With Binomial PD, Binomial CD, Poisson PD, and Poisson CD, you can input sample data and then perform calculations.
4. After inputting values for all of the variables, press  .
.
This displays the calculation results.
Pressing  or
or  while a calculation result is displayed will return to the input screen of the first variable.
while a calculation result is displayed will return to the input screen of the first variable.
Note
To change the distribution calculation type after you enter the DIST Mode, press 
 (STAT/DIST)
(STAT/DIST) (Type) and then select the distribution type you want.
(Type) and then select the distribution type you want.
Distribution calculation accuracy is up to five significant digits.
Variables that Accept Input
The following are distribution calculation variables that accept input values.
Normal PD ........................... x, σ, μ
Normal CD ........................... Lower, Upper, σ, μ
Inverse Normal .................... Area, σ, μ (Tail setting always left.)
Binomial PD, Binomial CD ... x (or List), N, p
Poisson PD, Poisson CD ..... x (or List), μ
x: data
σ: standard deviation (σ < 0)
μ: mean
Lower: lower boundary
Upper: upper boundary
Tail: probability value tail specification
Area: probability value (0 ≦ Area ≦ 1)
List: sample data list
N: number of trials
p: success probability (0 ≦ p ≦ 1)
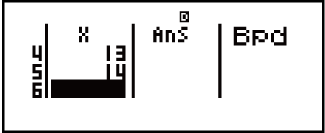
List Screen (Binomial PD, Binomial CD, Poisson PD, Poisson CD)
With Binomial PD, Binomial CD, Poisson PD, and Poisson CD, use the List Screen for sample data input. You can input up to 25 data samples for each variable. Calculation results are also displayed on the List Screen.
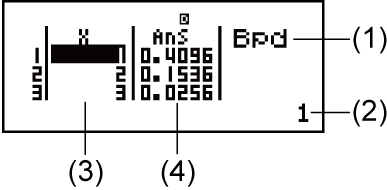 (1) Distribution calculation type
(1) Distribution calculation type
(2) Value at current cursor position
(3) X: Sample data
(4) Ans: Calculation results
To edit sample data:
Move the cursor to the cell that contains the data you want to edit, input the new data, and then press  .
.
To delete data:
Move the cursor to the sample data you want to delete and then press  .
.
To insert sample data:
Move the cursor to the position where you want to insert the sample data, press 
 (STAT/DIST)
(STAT/DIST) (Edit)
(Edit) (Ins), and then input the sample data.
(Ins), and then input the sample data.
To delete all sample data:
Press 
 (STAT/DIST)
(STAT/DIST) (Edit)
(Edit) (Del-A).
(Del-A).
DIST Mode Calculation Examples
Example 1: To calculate the normal probability density when x = 36, σ = 2, μ = 35


 (DIST)
(DIST)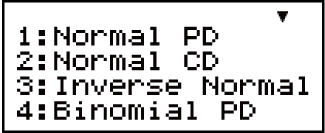
 (Normal PD)
(Normal PD)
- 36


- 2


- 35

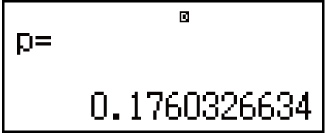
Result: 0.1760326634
Pressing  or
or  returns to the x input screen.
returns to the x input screen.
Example 2: To calculate binomial probability for the sample data {10, 11, 12, 13, 14} when N = 15 and p = 0.6


 (DIST)
(DIST) (Binomial PD)
(Binomial PD)
- Display the List Screen:
 (List)
(List) 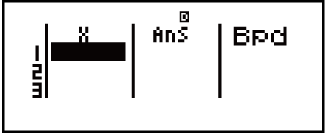
To specify data using parameter format, press  (Var).
(Var).
- 10
 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14
- 15


- 0
 6
6
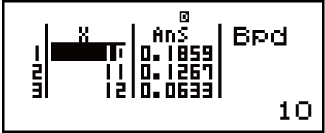
Results: x = binomial probability of 10 ≒ 0.18594
x = binomial probability of 11 ≒ 0.12678
x = binomial probability of 12 ≒ 0.063388
x = binomial probability of 13 ≒ 0.021942
x = binomial probability of 14 ≒ 4.7018 × 10-3
Pressing  returns to the N input screen. Pressing
returns to the N input screen. Pressing  returns to the List Screen (input data samples are stored).
returns to the List Screen (input data samples are stored).
Note
The following cannot be used in the distribution calculations: Pol, Rec, ÷R, ∫, d/dx.
When data is specified using parameter format, calculation results are stored in Ans memory.
An error message appears if the input value is outside the allowable range. "ERROR" will appear in the Ans column of the List Screen when the value input for the corresponding sample data is outside the allowable range.