fx-100MS/fx-570MS/
fx-991MS/
(2nd edition / S-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Basic Calculations
- ▶Inputting Expression and Values
- ▶Arithmetic Calculations
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Using Engineering Symbols
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial (!)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding function (Rnd)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
- ▶Metric Conversion (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (SD, REG)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MAT) (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VCT) (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
Technical Information
Base-n Calculations (BASE)
Base-n Calculation Examples
Example 1: To calculate 101112 + 110102 in binary (1100012)
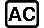
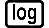 (BIN) 10111
(BIN) 10111 11010
11010
- 110001
Example 2: To calculate 78 + 18 in octal (108)
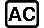
 (OCT) 7
(OCT) 7 1
1
- 10
Example 3: To calculate 1F16 + 116 in hexadecimal (2016)
 (HEX) 1
(HEX) 1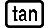 (F)
(F) 1
1
- 20
Example 4: To convert the decimal value 3010 to binary, octal, and hexadecimal
 (DEC) 30
(DEC) 30
- 30
 (BIN)
(BIN)- 11110
 (OCT)
(OCT)- 36
 (HEX)
(HEX)- 1E
Example 5: To transform the result of 510 + 516 to binary
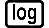 (BIN)
(BIN) 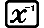 (LOGIC)
(LOGIC) (LOGIC)
(LOGIC) (LOGIC)
(LOGIC) (d) 5
(d) 5
 (LOGIC)
(LOGIC) (LOGIC)
(LOGIC) (LOGIC)
(LOGIC) (h) 5
(h) 5
- 1010