fx-100MS/fx-570MS/
fx-991MS/
(2nd edition / S-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Basic Calculations
- ▶Inputting Expression and Values
- ▶Arithmetic Calculations
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Using Engineering Symbols
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial (!)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding function (Rnd)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
- ▶Metric Conversion (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (SD, REG)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MAT) (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VCT) (fx-570MS/fx-991MS only)
Technical Information
Differential Calculations
The procedure described below obtains the derivative of a function.
Three inputs are required for the differential expression: the function of variable x, the point (a) at which the differential coefficient is calculated, and the change in x (Δx).
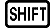
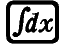 (d/dx) expression
(d/dx) expression  a
a 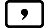 Δx
Δx 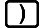
Example: To determine the derivative at point x = 2 for the function y = 3x2 - 5x + 2, when the increase or decrease in x is Δx = 2 × 10-4 (Result: 7)
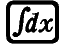 (d/dx) 3
(d/dx) 3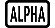
 (X)
(X)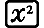
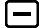 5
5
 (X)
(X) 2
2 2
2 2
2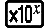
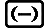 4
4

- 7.
Note
Differential calculations can be performed in the COMP Mode only.
You can omit input of Δx, if you want. The calculator automatically substitutes an appropriate value for Δx if you do not input one.
Discontinuous points and extreme changes in the value of x can cause inaccurate results and errors.
Select Rad (Radian) for the angle unit setting when performing trigonometric function differential calculations.