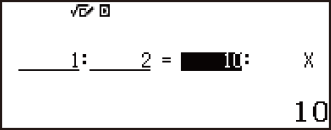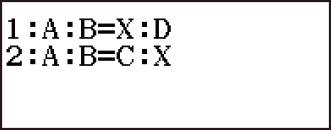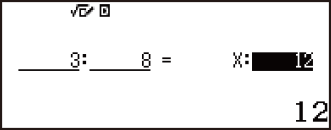fx-83GT X/fx-85GT X
CLASSWIZ
Scientific Calculator
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Inputting a Calculation Expression Using Values
- ▶Inputting an Expression Using Natural Textbook Format
(MathI/MathO or MathI/DecimalO Only) - ▶Displaying Calculation Results in a Form that Includes
√2, π, etc. (Irrational Number Form)
Basic Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Arithmetic Calculations
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Converting an Input Value to the Calculator’s Default Angle Unit
- ▶Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Calculation (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#), Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Statistical Calculations
- Inputting Data with Statistics Editor
- Statistical Calculation Screen
- Using the Statistical Menu
- Displaying Statistical Values Based On Input Data
- Displaying Regression Calculation Results Based On
Input Data (Paired-Variable Data Only) - Single-variable Statistical Calculation Commands
- Single-variable Statistical Calculation Examples
- Linear Regression Calculation (y=a+bx) Commands
- Linear Regression Calculation Examples
- Quadratic Regression Calculation (y=a+bx+cx2) Commands
- Quadratic Regression Calculation Examples
- Logarithmic Regression Calculation (y=a+b・ln(x)) Commands
- Logarithmic Regression Calculation Examples
- e Exponential Regression Calculation (y=a・e^(bx)) Commands
- e Exponential Regression Calculation Examples
- ab Exponential Regression Calculation (y=a・b^x) Commands
- ab Exponential Regression Calculation Examples
- Power Regression Calculation (y=a・x^b) Commands
- Power Regression Calculation Examples
- Inverse Regression Calculation (y=a+b/x) Commands
- Inverse Regression Calculation Examples
- ▶Creating a Number Table
- ▶Ratio Calculations
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Stack Limitations
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
Frequently Asked Questions
Ratio Calculations
The Ratio Mode lets you determine the value of X in the ratio expression A : B = X : D (or A : B = C : X) when the values of A, B, C and D are known. The following shows the general procedure for using Ratio.
1. Press  , select the Ratio Mode icon, and then press
, select the Ratio Mode icon, and then press  .
.
2. On the menu that appears, select  (A:B=X:D) or
(A:B=X:D) or  (A:B=C:X).
(A:B=C:X).
3. On the Coefficient Editor screen that appears, input up to 10 digits for each of the required values (A, B, C, D).
To solve 3 : 8 = X : 12 for X, for example, press  in step 1, and then input the following for the coefficients (A = 3, B = 8, D = 12): 3
in step 1, and then input the following for the coefficients (A = 3, B = 8, D = 12): 3 8
8 12
12 .
.
Pressing  will reset all of the coefficients to one.
will reset all of the coefficients to one.
4. After all the values are the way you want, press  .
.
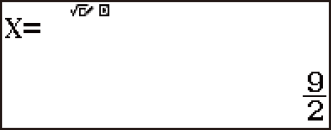
This displays the solution (value of X).
Pressing  again will return to the Coefficient Editor.
again will return to the Coefficient Editor.
Important!
A Math ERROR will occur if you perform a calculation while 0 is input for a coefficient.
Changing the Ratio Expression Type
Press 
 (Select Type) and then select the ratio expression type you want from the menu that appears. Changing the ratio expression type causes the values of all Coefficient Editor coefficients to change to one.
(Select Type) and then select the ratio expression type you want from the menu that appears. Changing the ratio expression type causes the values of all Coefficient Editor coefficients to change to one.
Ratio Mode Calculation Example
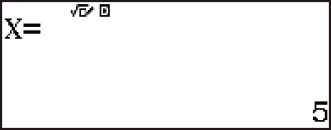
Example 1: To calculate X in the ratio 1 : 2 = X : 10

 (Select Type)
(Select Type) (A:B=X:D)
(A:B=X:D)
1 2
2 10
10
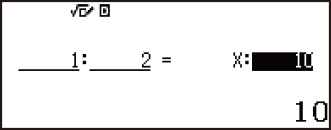
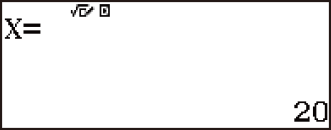
Example 2: To calculate X in the ratio 1 : 2 = 10 : X

 (Select Type)
(Select Type) (A:B=C:X)
(A:B=C:X)
1 2
2 10
10