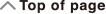fx-83GT X/fx-85GT X
CLASSWIZ
Scientific Calculator
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Inputting a Calculation Expression Using Values
- ▶Inputting an Expression Using Natural Textbook Format
(MathI/MathO or MathI/DecimalO Only) - ▶Displaying Calculation Results in a Form that Includes
√2, π, etc. (Irrational Number Form)
Basic Calculations
- ▶Recurring Decimal Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Arithmetic Calculations
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Converting an Input Value to the Calculator’s Default Angle Unit
- ▶Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Calculation (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#), Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Statistical Calculations
- Inputting Data with Statistics Editor
- Statistical Calculation Screen
- Using the Statistical Menu
- Displaying Statistical Values Based On Input Data
- Displaying Regression Calculation Results Based On
Input Data (Paired-Variable Data Only) - Single-variable Statistical Calculation Commands
- Single-variable Statistical Calculation Examples
- Linear Regression Calculation (y=a+bx) Commands
- Linear Regression Calculation Examples
- Quadratic Regression Calculation (y=a+bx+cx2) Commands
- Quadratic Regression Calculation Examples
- Logarithmic Regression Calculation (y=a+b・ln(x)) Commands
- Logarithmic Regression Calculation Examples
- e Exponential Regression Calculation (y=a・e^(bx)) Commands
- e Exponential Regression Calculation Examples
- ab Exponential Regression Calculation (y=a・b^x) Commands
- ab Exponential Regression Calculation Examples
- Power Regression Calculation (y=a・x^b) Commands
- Power Regression Calculation Examples
- Inverse Regression Calculation (y=a+b/x) Commands
- Inverse Regression Calculation Examples
- ▶Creating a Number Table
- ▶Ratio Calculations
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Stack Limitations
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
Frequently Asked Questions
Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
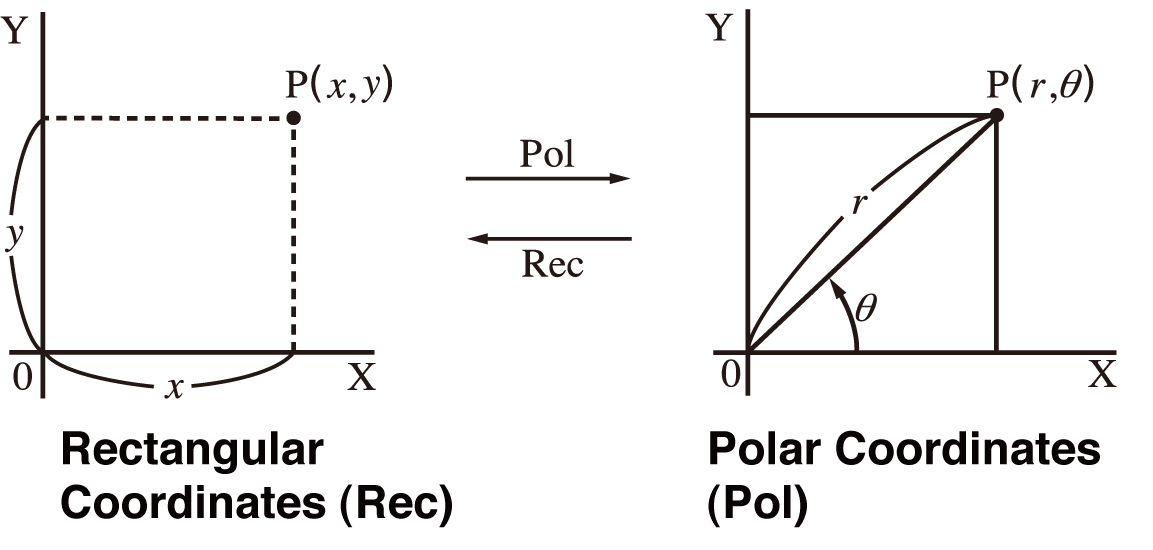
Coordinate conversion can be performed in the Calculate and Statistics calculation modes.
Pol converts rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates, while Rec converts polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates.
Specify the angle unit before performing calculations.
Converting to Polar Coordinates (Pol)
Pol(X, Y) X: Specifies the rectangular coordinate X value
Pol(X, Y) Y: Specifies the rectangular coordinate Y value
Calculation result θ is displayed in the range of -180° < θ < 180°.
Calculation result θ is displayed using the calculator’s angle unit.
Calculation result r is assigned to variable X, while θ is assigned to Y.
Converting to Rectangular Coordinates (Rec)
Rec(r, θ) r : Specifies the polar coordinate r value
Rec(r, θ) θ : Specifies the polar coordinate θ value
Input value θ is treated as an angle value, in accordance with the calculator’s angle unit setting.
Calculation result x is assigned to variable X, while y is assigned to Y.
If you perform coordinate conversion inside of an expression instead of a stand-alone operation, the calculation is performed using only the first value (either the r-value or the X-value) produced by the conversion.
Example: Pol (√2, √2) + 5 = 2 + 5 = 7
Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion Examples
Example 1: (X, Y) = (√2, √2) → (r, θ) (Angle Unit: Degree)
(MathI/MathO)

 (Pol)
(Pol) 2
2

 (,)
(,) 2
2


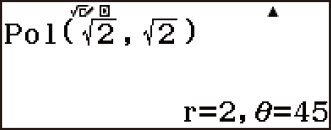
(LineI/LineO)

 (Pol)
(Pol) 2
2

 (,)
(,) 2
2


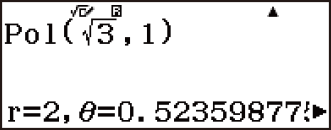
Example 2: (X, Y) = (√3, 1) → (r, θ) (Angle Unit: Radian)
(MathI/MathO)

 (Pol)
(Pol) 3
3

 (,) 1
(,) 1

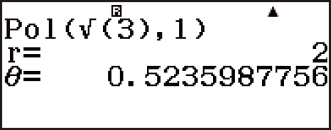
(LineI/LineO)

 (Pol)
(Pol) 3
3

 (,) 1
(,) 1

Example 3: (r, θ) = (√2, 45) → (X, Y) (Angle Unit: Degree)
(MathI/MathO)

 (Rec)
(Rec) 2
2

 (,) 45
(,) 45

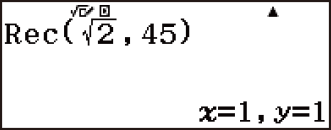
(LineI/LineO)

 (Rec)
(Rec) 2
2

 (,) 45
(,) 45


Example 4: (r, θ) = (2, π6) → (X, Y) (Angle Unit: Radian)
(MathI/MathO)

 (Rec)
(Rec)
2
 (,)
(,)
 (π)
(π) 6
6



(LineI/LineO)

 (Rec) 2
(Rec) 2
 (,)
(,)
 (π)
(π) 6
6