fx-82MS
fx-85MS
fx-220 PLUS
fx-300MS
fx-350MS
(2nd edition / S-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Basic Calculations
- ▶Inputting Expression and Values
- ▶Arithmetic Calculations
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements (fx-82MS/fx-85MS/fx-300MS/fx-350MS only)
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial (!)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#) (fx-220 PLUS only)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding function (Rnd)
Using Calculation Modes
Technical Information
Using Memory Functions
Answer Memory (Ans)
Whenever you press  after inputting values or an expression, the calculated result automatically updates Answer Memory contents by storing the result.
after inputting values or an expression, the calculated result automatically updates Answer Memory contents by storing the result.
fx-82MS/fx-85MS/fx-300MS/fx-350MS: In addition to  , Answer Memory contents are also updated with result whenever you press
, Answer Memory contents are also updated with result whenever you press 
 (%),
(%),  ,
, 
 (M-), or
(M-), or 
 (STO) followed by a letter (A through F, or M, X, or Y).
(STO) followed by a letter (A through F, or M, X, or Y).
fx-220 PLUS: In addition to  , Answer Memory contents are also updated
with result whenever you press
, Answer Memory contents are also updated
with result whenever you press 
 (%),
(%),  ,
, 
 (M-), or
(M-), or 
 (Min).
(Min).
You can recall Answer Memory contents by pressing 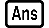 .
.
Answer Memory can store up to 15 digits for the mantissa and two digits for the exponent.
Answer Memory contents are not updated if the operation performed by any of the above key operations results in an error.
Consecutive Calculations
You can use the calculation result that is currently on the display (and also stored in Answer Memory) as the first value of your next calculation. Note that pressing an operator key while a result is displayed causes the displayed value to change to Ans, indicating it is the value that is currently stored in Answer Memory.
The result of a calculation can also be used with a subsequent Type A function (x2, x3, x-1, x!, DRG ), +, -, xy, x√ , ×, ÷, nPr and nCr.
), +, -, xy, x√ , ×, ÷, nPr and nCr.
Example 1: To divide the result of 3 × 4 by 30
- 3
 4
4
- 12.
- (Continuing)
 30
30

Example 2: To perform the calculations shown below:
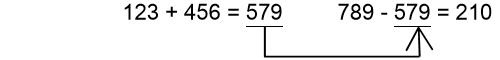
- 123
 456
456
- 579.
- (Continuing) 789

- 210.