fx-82MS
fx-85MS
fx-220 PLUS
fx-300MS
fx-350MS
(2nd edition / S-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Basic Calculations
- ▶Inputting Expression and Values
- ▶Arithmetic Calculations
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements (fx-82MS/fx-85MS/fx-300MS/fx-350MS only)
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial (!)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#) (fx-220 PLUS only)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding function (Rnd)
Using Calculation Modes
Technical Information
Using Engineering Notation
A simple key operation transforms a displayed value to engineering notation.
Example 1: To convert 56088 meters to kilometers → 56.088 × 103 (km)
- 56088

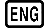
- 56.088×1003
Example 2: To convert 0.08125 grams to milligrams → 81.25 × 10-3 (mg)
- 0
 08125
08125
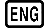
- 81.25×10-03
Example 3: Transform the value 1234 to engineering notation, shifting the decimal point to the right.
- 1234

- 1234.
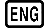
- 1.234×1003
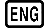
- 1234.×1000
Example 4: Transform the value 123 to engineering notation, shifting the decimal point to the left.
- 123

- 123.
 (←)
(←)- 0.123×1003
 (←)
(←)- 0.000123×1006