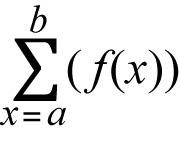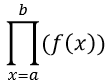Function Analysis
This section explains commands and functions that you can input after performing the operation:  – [Func Analysis].
– [Func Analysis].
Summation(Σ)
With Σ(, you can obtain the sum of an input f(x) expression for a specific range.
Note
This function can be used with any of the following calculator apps: Calculate, Statistics, Distribution, Table, Vector.
Input Syntax
The input syntax depends on the Input/Output setting on the SETTINGS menu, as shown in the table below.
| Input/Output setting | Input Syntax |
|---|---|
| MathI/MathO or MathI/DecimalO |
|
| LineI/LineO or LineI/DecimalO |
|
* a and b are integers that can be specified within the range of -1 × 1010 < a ≤ b < 1 × 1010.
Σ Calculation Example
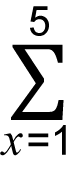 (x + 1) = 20
(x + 1) = 20
(Input/Output: MathI/MathO)
 – [Func Analysis] > [Summation(Σ)]
– [Func Analysis] > [Summation(Σ)]

 1
1 1
1 5
5

(Input/Output: LineI/LineO)
 – [Func Analysis] > [Summation(Σ)]
– [Func Analysis] > [Summation(Σ)]

 1
1
 (,)1
(,)1
 (,)5
(,)5

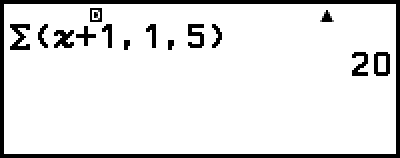
Product(Π)
With ∏(, you can obtain the product of an input f(x) expression for a specific range.
Note
This function can be used with any of the following calculator apps: Calculate, Statistics, Distribution, Table, Vector.
Input Syntax
The input syntax depends on the Input/Output setting on the SETTINGS menu, as shown in the table below.
| Input/Output setting | Input Syntax |
|---|---|
| MathI/MathO or MathI/DecimalO |
|
| LineI/LineO or LineI/DecimalO | Π(f(x), a, b)* |
* a and b are integers that can be specified within the range of a < 1 × 1010, b < 1 × 1010, a ≤ b.
∏ Calculation Example
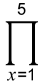 (x + 1) = 720
(x + 1) = 720
(Input/Output: MathI/MathO)
 – [Func Analysis] > [Product(Π)]
– [Func Analysis] > [Product(Π)]

 1
1 1
1 5
5

(Input/Output: LineI/LineO)
 – [Func Analysis] > [Product(Π)]
– [Func Analysis] > [Product(Π)]

 1
1
 (,)1
(,)1
 (,)5
(,)5


Logarithm(logab), Logarithm(log)
Use 
 (log) or
(log) or  – [Func Analysis] > [Logarithm(log)] to input logab as log (a, b). Base 10 is the initial default setting if you do not input anything for a.
– [Func Analysis] > [Logarithm(log)] to input logab as log (a, b). Base 10 is the initial default setting if you do not input anything for a.
Example 1: log101000 = log 1000 = 3

 (log)1000
(log)1000

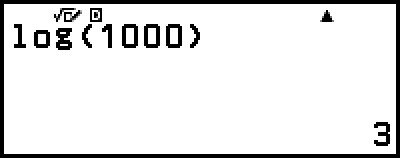
Example 2: log216 = 4

 (log)2
(log)2
 (,)16
(,)16


The  key (or
key (or  – [Func Analysis] > [Logarithm(logab)]) also can be used for input, but only while MathI/MathO or MathI/DecimalO is selected for Input/Output on the SETTINGS menu. In this case, you must input a value for the base.
– [Func Analysis] > [Logarithm(logab)]) also can be used for input, but only while MathI/MathO or MathI/DecimalO is selected for Input/Output on the SETTINGS menu. In this case, you must input a value for the base.
Example 3: log216 = 4
 2
2 16
16

Natural Logarithm
Use 
 (ln) or
(ln) or  – [Func Analysis] > [Natural Logarithm] to input "ln".
– [Func Analysis] > [Natural Logarithm] to input "ln".
Example: ln 90 (= loge90) = 4.49980967

 (ln)90
(ln)90