Probability
This section explains commands and functions that you can input after performing the operation:  – [Probability].
– [Probability].
%
Inputting a value followed by % command causes the input value to become a percent.
Example 1: 150 × 20% = 30
- 150
 20
20
 – [Probability] > [%]
– [Probability] > [%]

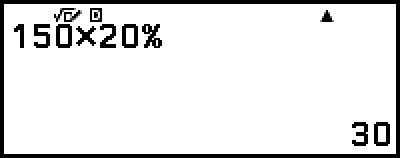
Example 2: Calculate what percentage of 880 is 660. (75%)
- 660
 880
880
 – [Probability] > [%]
– [Probability] > [%]


Example 3: Discount 3500 by 25%. (2625)
- 3500
 3500
3500 25
25
 – [Probability] > [%]
– [Probability] > [%]

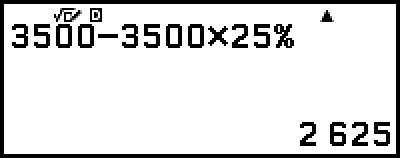
Factorial(!)
This function obtains the factorials of a value that is zero or a positive integer.
Example: (5 + 3)! = 40320
 5
5 3
3
 – [Probability] > [Factorial(!)]
– [Probability] > [Factorial(!)]


Permutation(P), Combination(C)
Permutation (nPr) and combination (nCr) functions.
Example: To determine the number of permutations and combinations possible when selecting four people from a group of 10
Permutations:
- 10
 – [Probability] > [Permutation(P)]
– [Probability] > [Permutation(P)]
4

Combinations:
- 10
 – [Probability] > [Combination(C)]
– [Probability] > [Combination(C)]
4

Random Number
This function generates a pseudo random number in the range of 0.000 to 0.999. The result is displayed as a fraction when MathI/MathO is selected for Input/Output on the SETTINGS menu.
Example: To obtain random three-digit integers
- 1000
 – [Probability] > [Random Number]
– [Probability] > [Random Number]


- (The result differs with each execution.)
Random Integer
This function generates a pseudo random integer between a specified start value and end value.
Example: To generate random integers in the range of 1 to 6
 – [Probability] > [Random Integer]
– [Probability] > [Random Integer]
1
 (,)6
(,)6


- (The result differs with each execution.)
