Angle Unit, Polar/Rectangular Coordinate, Sexagesimal
This section explains commands, functions, and symbols that you can input after performing the operation:  – [Angle/Coord/Sexa].
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa].
Degrees, Radians, Gradians
These functions specify the angle unit.
° specifies degree, r radian, and g gradian.
You can input each function using the menu items below.
 – [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Degrees]
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Degrees]
 – [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Radians]
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Radians]
 – [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Gradians]
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Gradians]
Example: π/2 radians = 90° (Angle Unit: Degree)

 (π)
(π) 2
2
 – [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Radians]
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Radians]


Rect to Polar, Polar to Rect
"Pol(" converts rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates, while "Rec(" converts polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates.

Specify the Angle Unit on the SETTINGS menu before performing calculations.
The calculation result for r and θ and for x and y are each stored respectively to variables x and y.
Calculation result θ is displayed in the range of -180° < θ ≤ 180°.
Note
Pol( and Rec( can be used on the calculation screen of the calculator apps below.
Calculate, Statistics
Example 1: To convert rectangular coordinates (√2, √2) to polar coordinates (Input/Output: MathI/MathO, Angle Unit: Degree)
 – [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Rect to Polar]
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Rect to Polar]
 2
2

 (,)
(,) 2
2


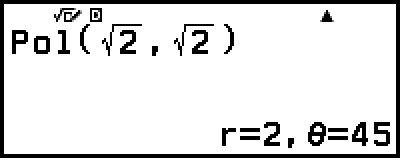
Example 2: To convert polar coordinates (√2, 45°) to rectangular coordinates (Input/Output: MathI/MathO, Angle Unit: Degree)
 – [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Polar to Rect]
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Polar to Rect]
 2
2

 (,) 45
(,) 45

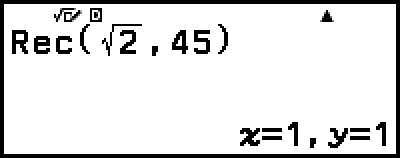
Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
You can use the keys or the menu item below to input the sexagesimal symbol (![]() ).
).

 (
( )
)
 – [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Degs Mins Secs] For details, see "Sexagesimal Conversion (Degree, Minute, Second Calculations)".
– [Angle/Coord/Sexa] > [Degs Mins Secs] For details, see "Sexagesimal Conversion (Degree, Minute, Second Calculations)".
