fx-570ES PLUS
fx-991ES PLUS
fx-9910NG PLUS
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶√ Form Calculation Range
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Integration Calculations
- ▶Differential Calculations
- ▶Σ Calculations
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Using CALC
- ▶Using SOLVE
- ▶Scientific Constants
- ▶Metric Conversion
Using Calculation Modes
- ▶Complex Number Calculations (CMPLX)
- ▶Statistical Calculations (STAT)
- ▶Base-n Calculations (BASE-N)
- ▶Equation Calculations (EQN)
- ▶Matrix Calculations (MATRIX)
- ▶Creating a Numerical Table from a Function (TABLE)
- ▶Vector Calculations (VECTOR)
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Metric Conversion
The calculator's built-in metric conversion commands make it simple to convert values from one unit to another. You can use the metric conversion commands in any calculation mode except for BASE-N and TABLE.
To input a metric conversion command into a calculation, press 
 (CONV) and then input the two-digit number that corresponds to the command you want.
(CONV) and then input the two-digit number that corresponds to the command you want.
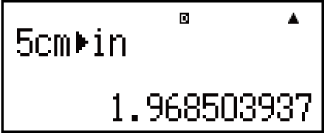
Example 1: To convert 5 cm into inches (LineIO)
 5
5
 (CONV)
(CONV)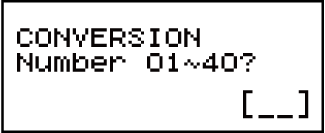

 (cm
(cm in)
in)
Example 2: To convert 100 g into ounces (LineIO)
 100
100
 (CONV)
(CONV)
 (g
(g oz)
oz)

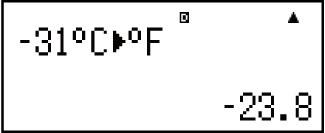
Example 3: To convert -31°C into Fahrenheit (LineIO)

 31
31
 (CONV)
(CONV)
 (°C
(°C °F)
°F)
The following shows the two-digit numbers for each of the metric conversion commands.
01: in cm cm |
02: cm in in |
03: ft m m |
04: m ft ft |
05: yd m m |
06: m yd yd |
07: mile km km |
08: km mile mile |
09: n mile m m |
10: m n mile n mile |
11: acre m2 m2 |
12: m2 acre acre |
13: gal (US) ℓ ℓ |
14: ℓ gal (US) gal (US) |
15: gal (UK) ℓ ℓ |
16: ℓ gal (UK) gal (UK) |
17: pc km km |
18: km pc pc |
19: km/h m/s m/s |
20: m/s km/h km/h |
21: oz g g |
22: g oz oz |
23: lb kg kg |
24: kg lb lb |
25: atm Pa Pa |
26: Pa atm atm |
27: mmHg Pa Pa |
28: Pa mmHg mmHg |
29: hp kW kW |
30: kW hp hp |
31: kgf/cm2 Pa Pa |
32: Pa kgf/cm2 kgf/cm2 |
33: kgf • m J J |
34: J kgf • m kgf • m |
35: lbf/in2 kPa kPa |
36: kPa lbf/in2 lbf/in2 |
37: °F °C °C |
38: °C °F °F |
39: J cal cal |
40: cal J J |
Conversion formula data is based on the "NIST Special Publication 811 (2008)".
Note
The J cal command performs conversion for values at a temperature of 15°C.
cal command performs conversion for values at a temperature of 15°C.