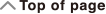fx-95MS/fx-500MS/
(2nd edition / S-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Basic Calculations
- ▶Inputting Expression and Values
- ▶Arithmetic Calculations
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial (!)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding function (Rnd)
Using Calculation Modes
Technical Information
Equation Calculations (EQN)
Quadratic and Cubic Equations
Quadratic Equation: ax2 + bx + c = 0
Cubic Equation: ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0
Entering the EQN Mode and pressing  displays the initial quadratic/cubic equation screen.
displays the initial quadratic/cubic equation screen.

Use this screen to specify 2 (quadratic) or 3 (cubic) as the degree of the equation, and input values for each of the coefficients.
(1) Coefficient name
(2) Element value
(3) Arrow indicates direction you should scroll to view other elements.
Any time until you input a value for the final coefficient (c for a quadratic equation, d for a cubic equation), you can use the  and
and  keys to move between coefficients on the screen and make changes, if you want.
keys to move between coefficients on the screen and make changes, if you want.
Note that you cannot input complex numbers for coefficients.
Calculation starts and one of the solutions appears as soon as you input a value for the final coefficient.
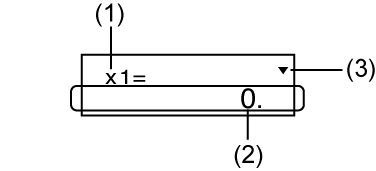
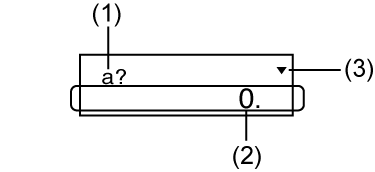
(1) Variable name
(2) Solution
(3) Arrow indicates direction you should scroll to view other solutions.
Press the  key to view other solutions. Use
key to view other solutions. Use  and
and  to scroll between all of the solutions for the equation.
to scroll between all of the solutions for the equation.
Pressing the  key at this point returns to the coefficient input screen.
key at this point returns to the coefficient input screen.
Certain coefficients can cause calculation to take more time.
Example 1: To solve the equation
x3 - 2x2 - x + 2 = 0 (x = 2, -1, 1)
| (Degree?) | 3 |
|---|---|
| (a?) | 1 |
| (b?) |  2 2  |
| (c?) |  1 1  |
| (d?) | 2  |
| (x1 = 2) |  |
| (x2 = -1) |  |
| (x3 = 1) |
If a result is a complex number, the real part of the first solution appears first. This is indicated by the "R↔I" symbol on the display. Press 
 (Re⇔Im) to toggle the display between the real part and imaginary part of a solution.
(Re⇔Im) to toggle the display between the real part and imaginary part of a solution.
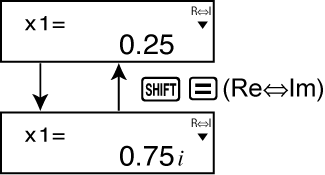
Example 2: To solve the equation
8x2 - 4x + 5 = 0 (x = 0.25 ± 0.75i)
| (Degree?) | 2 |
|---|---|
| (a?) | 8  |
| (b?) |  4 4 |
| (c?) | 5 |
| (x1 = 0.25 + 0.75i) |  |
| (x2 = 0.25 - 0.75i) |