fx-82AU PLUS II
(2nd edition / NATURAL-V.P.A.M.)
Before Using the Calculator
Calculation Modes and Calculator Setup
Inputting Expressions and Values
- ▶Basic Input Rules
- ▶Inputting with Natural Display
- ▶Using Values and Expressions as Arguments (Natural Display only)
- ▶Overwrite Input Mode (Linear Display only)
- ▶Correcting and Clearing an Expression
Basic Calculations
- ▶Toggling Calculation Results
- ▶Fraction Calculations
- ▶Percent Calculations
- ▶Degree, Minute, Second (Sexagesimal) Calculations
- ▶Multi-Statements
- ▶Using Engineering Notation
- ▶Prime Factorization
- ▶Calculation History and Replay
- ▶Using Memory Functions
Function Calculations
- ▶Pi (π), Natural Logarithm Base e
- ▶Trigonometric Functions
- ▶Hyperbolic Functions
- ▶Angle Unit Conversion
- ▶Exponential Functions
- ▶Logarithmic Functions
- ▶Power Functions and Power Root Functions
- ▶Rectangular-Polar Coordinate Conversion
- ▶Factorial Function (!)
- ▶Absolute Value Function (Abs)
- ▶Random Number (Ran#)
- ▶Random Integer (RanInt#)
- ▶Permutation (nPr) and Combination (nCr)
- ▶Rounding Function (Rnd)
- ▶Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Using Calculation Modes
Technical Information
- ▶Errors
- ▶Before Assuming Malfunction of the Calculator...
- ▶Replacing the Battery
- ▶Calculation Priority Sequence
- ▶Calculation Ranges, Number of Digits, and Precision
- ▶Specifications
- ▶Verifying the Authenticity of Your Calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
Using Memory Functions
Answer Memory (Ans)
The last calculation result obtained is stored in Ans(answer) memory.
Ans memory contents are updated whenever a new calculation result is dispalayed.
Answer Memory contents are updated whenever you execute a calculation using any one of the following keys:  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
, 
 (M-),
(M-),  ,
, 
 (STO).
(STO).
Answer Memory can hold up to 15 digits.
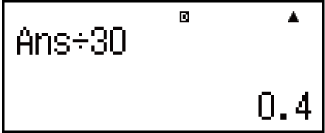
Example 1: To divide the result of 3 × 4 by 30 (LineIO)
- 3
 4
4
- 12
- (Continuing)
 30
30
Example 2: To perform the calculations shown below:
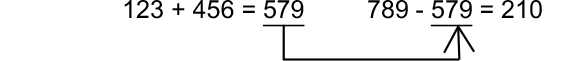 (MthIO-LineO)
(MthIO-LineO)- 123
 456
456
- 579
- (Continuing) 789




Variables (A, B, C, D, E, F, M, X, Y)
Your calculator has nine preset variables named A, B, C, D, E, F, M, X, and Y.
You can assign values to variables and use the variables in calculations.
Example:
To assign the result of 3 + 5 to variable A
- 3
 5
5
 (STO)
(STO) (A)
(A) - 8
To multiply the contents of variable A by 10
- (Continuing)
 (A)
(A) 10
10
- 80
To recall the contents of variable A
- (Continuing)

 (A)
(A) - 8
To clear the contents of variable A
- 0
 (STO)
(STO) (A)
(A) - 0
Independent Memory (M)
You can add calculation results to or subtract results from independent memory.
The "M" indicator appears on the display when there is any value other than zero stored in independent memory.
Example:
To clear the contents of M
- 0
 (STO)
(STO) (M)
(M) - 0
To add the result of 10 × 5 to M
- (Continuing) 10
 5
5
- 50
To subtract the result of 10 + 5 from M
- (Continuing) 10
 5
5
 (M-)
(M-) - 15
To recall the contents of M
- (Continuing)

 (M)
(M) - 35
Note
Variable M is used for independent memory.
Clearing the Contents of All Memories
Ans memory, independent memory, and variable contents are retained even if you press  , change the calculation mode, or turn off the calculator.
, change the calculation mode, or turn off the calculator.
Perform the following procedure when you want to clear the contents of all memories.
 (CLR)
(CLR) (Memory)
(Memory) (Yes)
(Yes)