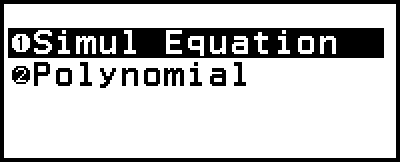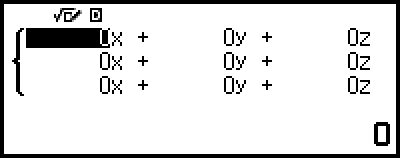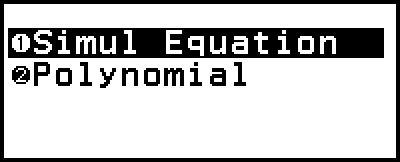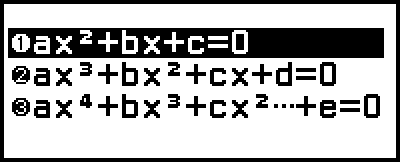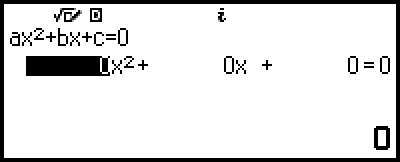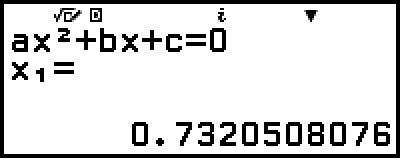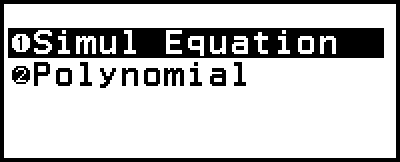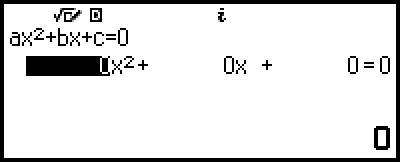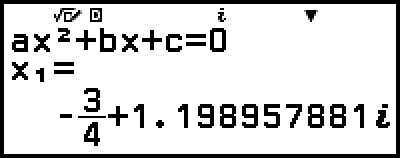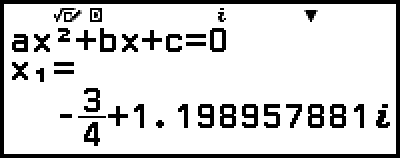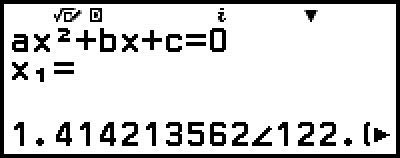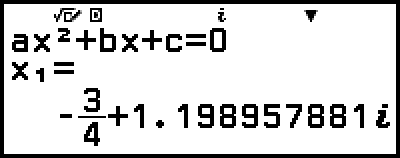Equation Calculations
The Equation app includes the two functions described below. After starting up the app, you can use the Equation menu that appears to select the function you want.
Simul Equation: Simultaneous linear equations with two to four unknowns
Polynomial: High-order equations from 2nd to 4th degree
Simultaneous Linear Equations
Here, we explain the general procedure for solving a simultaneous equation with an example that solves a simultaneous linear equation with three unknowns.
Example 1: 
1. Press  , select the Equation app icon, and then press
, select the Equation app icon, and then press  .
.
This displays the Equation menu.
2. Select [Simul Equation], and then press  .
.
This displays the number of unknowns menu.
3. Select [3 Unknowns], and then press  .
.
This displays the Coefficient Editor.
4. Use the Coefficient Editor to input coefficient values.
- 1


 ((-))1
((-))1 1
1 2
2
1 1
1

 ((-))1
((-))1 0
0

 ((-))1
((-))1 1
1 1
1 4
4
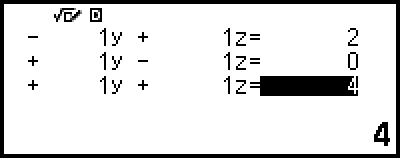
Pressing  while the Coefficient Editor is displayed will clear all of the coefficients to zero.
while the Coefficient Editor is displayed will clear all of the coefficients to zero.
5. Press  .
.
This will display a solution.
While the  indicator is displayed, each press of
indicator is displayed, each press of  (or
(or  ) will display another solution.
) will display another solution.
 (or
(or  )
) 
 (or
(or  )
) 
Pressing  or
or  while the
while the  indicator is displayed causes the previously displayed solution to reappear.
indicator is displayed causes the previously displayed solution to reappear.
Pressing  while the final solution is displayed returns to the Coefficient Editor. To return to the Coefficient Editor while any solution is displayed, press
while the final solution is displayed returns to the Coefficient Editor. To return to the Coefficient Editor while any solution is displayed, press  .
.
Pressing  while the Coefficient Editor is displayed returns to the number of unknowns menu.
while the Coefficient Editor is displayed returns to the number of unknowns menu.
Note
While the Coefficient Editor is displayed, you can store the currently highlighted value to a variable. Also, while the solution is being displayed, the currently displayed solution can be stored to a variable. For details about variables, see "Variables (A, B, C, D, E, F, x, y, z)".
High-order Equations from 2nd to 4th Degree
When you solve a high-order equation with the Equation app, the values below are displayed according to the degree of the equation.
Quadratic Equation
The solution of ax2+bx+c=0 is displayed.
Cubic Equation
The solution of ax3+bx2+cx+d=0 is displayed.
Quartic Equation
The solution of ax4+bx3+cx2+dx+e=0 is displayed.
Here we will show an example of a quadratic equation to explain the general procedure for solving a high-order equation.
Example 2: x2 + 2x − 2 = 0
(Input/Output: MathI/MathO)
1. Press  , select the Equation app icon, and then press
, select the Equation app icon, and then press  .
.
This displays the Equation menu.
2. Select [Polynomial], and then press  .
.
This displays the number of degrees menu.
3. Select [ax2+bx+c=0], and then press  .
.
This displays the Coefficient Editor.
4. Use the Coefficient Editor to input coefficient values.
- 1
 2
2

 ((-))2
((-))2
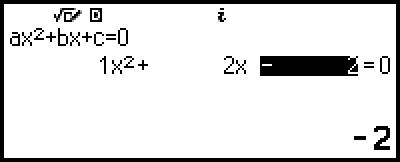
Pressing  while the Coefficient Editor is displayed will clear all of the coefficients to zero.
while the Coefficient Editor is displayed will clear all of the coefficients to zero.
5. Press  .
.
This will display a solution.
While the  indicator is displayed, each press of
indicator is displayed, each press of  (or
(or  ) will display another solution.
) will display another solution.
 (or
(or  )
) 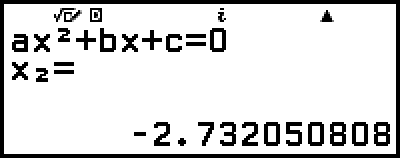
Pressing  or
or  while the
while the  indicator is displayed causes the previously displayed calculation result to appear again.
indicator is displayed causes the previously displayed calculation result to appear again.
Pressing  while the final calculation result is displayed returns to the Coefficient Editor. To return to the Coefficient Editor while any calculation result is displayed, press
while the final calculation result is displayed returns to the Coefficient Editor. To return to the Coefficient Editor while any calculation result is displayed, press  .
.
Pressing  while the Coefficient Editor is displayed returns to the number of degrees menu.
while the Coefficient Editor is displayed returns to the number of degrees menu.
Note
While the Coefficient Editor is displayed, you can store the currently highlighted value to a variable. Also, while a calculation result (solution or coordinate) is displayed, it can be stored to a variable. For details about variables, see "Variables (A, B, C, D, E, F, x, y, z)".
Complex Number Solution Display (Complex Roots)
High-order equations may have complex number solutions. When Polynomial is selected on the Equation menu, you can use the operations below to enable or disable complex number solution display.
 – [Complex Roots] > [On]
– [Complex Roots] > [On] 
Enables complex number solution display (initial default setting).
 – [Complex Roots] > [Off]
– [Complex Roots] > [Off] 
Disables complex number solution display. Inputting and executing an equation that has one or more complex number solutions only will cause the message "No Real Roots" to appear.
Example 3: 2x2 + 3x + 4 = 0
(Input/Output: MathI/MathO, Complex Result: a+bi, Complex Roots: On)
1. Press  , select the Equation app icon, and then press
, select the Equation app icon, and then press  .
.
This displays the Equation menu.
2. Select [Polynomial] > [ax2+bx+c=0].
This displays the Coefficient Editor.
3. Use the Coefficient Editor to input coefficient values.
- 2
 3
3 4
4

4. Press  .
.
This will display a solution.
5. Display another solution.
 (or
(or  )
) 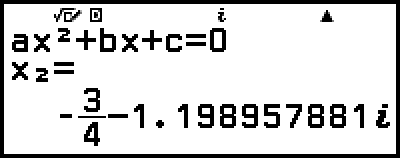
Pressing  while the final calculation result is displayed returns to the Coefficient Editor. To return to the Coefficient Editor while any calculation result is displayed, press
while the final calculation result is displayed returns to the Coefficient Editor. To return to the Coefficient Editor while any calculation result is displayed, press  .
.
Converting a Complex Number Solution to Rectangular or Polar Coordinates
You can use the FORMAT menu that appears when you press 
 (
( ) to convert a complex number solution to rectangular coordinate or polar coordinate format.
) to convert a complex number solution to rectangular coordinate or polar coordinate format.
Example 4: To convert the complex number solution displayed in Example 3 to polar coordinate format and then to rectangular coordinate format
1. Perform steps 1 to 4 of Example 3.
2. Press 
 (
( ), select [Polar Coord], and then press
), select [Polar Coord], and then press  .
.
This converts the solution to polar coordinate format.
3. Press 
 (
( ), select [Rectangular Coord], and then press
), select [Rectangular Coord], and then press  .
.
This converts the solution to rectangular coordinate format.