Differential Calculations
Function for approximation of the derivative based on the central difference method.
Natural Display input syntax is ddx (f (x)) | x=a, while Linear Display input syntax is ddx (f (x); a; tol).
tol specifies tolerance, which becomes 1 × 10-10 when nothing is input for tol.
Example 1: To obtain the derivative at point x = π/2 for the function y = sin(x) (Angle unit: Rad)
(MthIO-MathO)
 (
(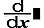 )
)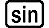
 (X)
(X)

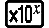 (π)
(π) 2
2
- 0
(LineIO)
 (
(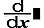 )
)
 (X)
(X)
 (;)
(;)
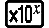 (π)
(π) 2
2

- 0
Example 2: ddx (3x2 - 5x + 2; 2; 1 × 10-12) = 7 (LineIO)
 (
(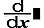 ) 3
) 3
 (X)
(X)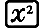
 5
5
 (X)
(X) 2
2
 (;)
(;)
2
 (;) 1
(;) 1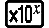
 12
12

- 7
Differential Calculation Precautions
Differential calculation can be performed in the COMP Mode only.
The following cannot be used in f(x): Pol, Rec, ÷R. The following cannot be used in f(x), a, b, or tol: ∫, d/dx, Σ.
When using a trigonometric function in f(x), specify Rad as the angle unit.
A smaller tol value increases precision, but it also increases calculation time. When specifying tol, use value that is 1 × 10-14 or greater.
If convergence to a solution cannot be found when tol input is omitted, the tol value will be adjusted automatically to determine the solution.
Non-consecutive points, abrupt fluctuation, extremely large or small points, inflection points, and the inclusion of points that cannot be differentiated, or a differential point or differential calculation result that approaches zero can cause poor precision or error.